Everything You Need To Know About An Amoxicillin Rash (and more)
Amoxicillin is among the most commonly prescribed antibiotics, frequently used for bacterial infections like ear infections, strep throat, and respiratory tract infections. While effective, amoxicillin can sometimes trigger a skin reaction, commonly known as an amoxicillin rash. Recent studies (2024) indicate approximately 5-10% of individuals taking amoxicillin experience some form of rash, though severity varies greatly based on individual sensitivity.
Most antibiotics can lead to expected side effects such as digestive problems in children and adults which include loose stools and nausea and vomiting. However, sometimes the adverse effects can cause a skin rash ranging from mild to severe and life threatening. Amoxicillin is a commonly used antibiotic that comes in the form of capsules and tablets. There are other formulations including amoxicillin-clavulanic acid which adds a chemical that makes it even more potent and less resistant to bacteria. One of the most commonly reported side effects of amoxicillin is a skin rash. As the skin is the largest organ in the body, this is at times the most visible when there is a reaction to this medication. As many as 25% of people taking amoxicillin according to research studies will develop a rash who take this medication.
Depending on the sensitivity of the individual to the medication, the severity and color of the rash can vary. It can spread across the body in the form of flat red or purple patches. Amoxicillin rash can also appear as tiny white and red bumps on the skin, raised and itchy and warm to the touch. Over time, the rash can darken in color, resembling a bruise. Blanching can occur in which the skin will lighten with the rash. When the rash is more severe, the rash will not lighten up when pressure on the skin is applied, indicating damage to the skin structure.
The antibiotic is derived from penicillin, which often leads to allergic reactions in some people. Usually when there is an allergy to a medication in this class, there will be allergy to amoxicillin as well. However, doctors and researchers still have to figure out what exactly causes an amoxicillin rash though it is likely to be immune mediated in which the body’s system has an abnormal reaction to the medication and releases inflammatory chemicals that cause the skin to be irritated as well.
In this article, we will learn what an amoxicillin rash looks like and what you can do to manage it effectively. We will also take a look at the possible reasons behind the development of the rash. So, let’s get right into it.
What Does An Amoxicillin Rash Look Like?
An amoxicillin rash can develop in two forms depending on the allergic reaction with each individual. It can either be a maculopapular rash or in the form of hives. Maculopapular means flat reddened areas with bumps that form a pattern within an area of the skin.
A maculopapular rash can occur any time after taking the medication. Immediate reactions can take 30 to 60 minutes to develop a rash, But it can be delayed and can also develop within three to ten days as the immune system starts to react over a period of time. You will notice flat pink or purple spots appearing in a symmetrical pattern all over your body. Contrary to popular belief, the rash isn’t contagious even though it will make others notice. It starts fading after three days and disappears completely within six days.
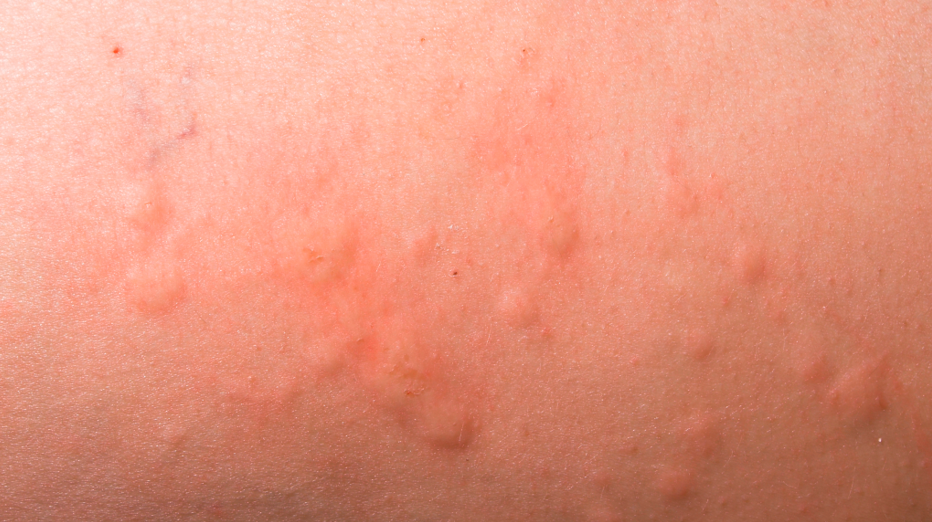
Some people develop hives after taking amoxicillin. It is basically an allergic reaction to penicillin. You may experience tiny bumps appearing on your different parts of your skin. These red bumps are itchy and keep changing their location. The picture above shows an example of hives and the texture is usually harder than the areas without hives.
Hives can spread and develop into a severe rash. If you notice any raised bumps or experience breathing problems after taking a dose of amoxicillin, contact your doctor or healthcare provider right away. These symptoms include anaphylaxis which can affect other organ systems including the respiratory system and circulatory. When severe, this can cause respiratory failure and circulatory failure. Medications to stop this process such as epinephrine and steroids are critical and require a medical health professional to prescribe and intervene immediately.
1. Maculopapular Rash:
- Flat, red, or purple patches scattered across the body.
- Often accompanied by small, raised bumps.
- Usually symmetrical, appearing on both sides of the body.
- Not typically itchy but can be mildly uncomfortable.
- Rash usually develops between 3-10 days after starting amoxicillin.
2. Hives (Urticaria):
- Can indicate a more serious allergic reaction.
- Raised, red or white itchy bumps.
- Hives can rapidly change locations, appearing and disappearing unpredictably.
- Usually occur within minutes to hours after antibiotic administration.
What Causes An Amoxicillin Rash?
Thanks to the advancement in medical research, not many children or adults get a skin rash from antibiotics nowadays. Researchers aren’t sure about how a maculopapular rash develops. However, hives are in many instances confirmed to be an allergic reaction to penicillin.
If you or your child develops a mild rash, it may be a slight reaction to the medication. You don’t need to worry about it but should monitor whether it develops further, and to make a note of it and let your medical provider know about a potential reaction.
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-based antibiotic, and reactions typically occur due to:
- Allergic Reactions: The immune system mistakes amoxicillin as harmful, releasing chemicals like histamine, causing hives and more severe reactions.
- Non-Allergic Immune Reactions: Mild maculopapular rashes are likely immune-mediated responses rather than true allergies, triggered by the body’s immune response to the medication.
How To Treat An Amoxicillin Rash?
Over-the-counter medications such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) are effective solutions for itchy rashes in the right circumstances, You should always consult with your doctor before taking an antibiotic or a treatment for drug induced rashes. It helps rule in or out any allergic reactions that you may have after taking the medication.
Unfortunately, the meaning and origin of a rash can be very confusing. A rash could mean an insignificant reaction that is temporary in nature or it could be the result of a severe allergy. If it is an strongallergic reaction, it can spread quickly and become severe and widespread. It may even put your life at risk. If the rash is spread across a large part of the body, it could be a sign of severe inflammation and at times it is treated like a burn on the skin. Stronger prescription and medications such as steroids are needed to calm the immune system from doing more damage. Therefore timely medical care is recommended as soon as possible if this should happen.
At times, a skin biopsy or skin test/allergen challenge is needed to confirm the presence of a drug induced allergy. Diluted challenges to penicillins that are given by a health professional in diluted samples can also help diagnose amoxicillin allergies. Unfortunately, allergies to penicillin class medications such as amoxicillin can also cause a cross sensitivity and allergy to other classes including cephalosporins such as ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, and cefoxitin. The same can be said if people are allergic to cephalosporins, and can react with penicillin class medications such as amoxicillin. People who become sensitized to penicillin classes can also develop further antibiotic class allergies to other common antibiotics. Caution should be used when taking other antibiotics once you have had a reaction to amoxicillin so check with your medical provider and alert them to any prior reaction to these medications.
In very rare instances, physicians use highly diluted amounts of amoxicillin to build resistance, known as densensitization therapy. In controlled settings usually in the hospital, monitoring while serial dilutions are given gradually so if penicillin based medications are needed, they can be given.
How Serious Is an Amoxicillin Rash?
Most amoxicillin rashes are mild and resolve without serious issues. However, a rash can occasionally indicate a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), which can be life-threatening.
Seek emergency help immediately if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or fainting
- Severe, widespread rash with blistering or skin peeling
Cross-Reactivity with Other Antibiotics
Individuals allergic to amoxicillin (penicillin class) may react to related antibiotics, particularly cephalosporins:
- Ceftriaxone
- Cefuroxime
- Cefoxitin
Always inform your healthcare provider if you’ve had previous reactions to antibiotics.
Takeaway
All in all, it’s important to consult with your doctor before starting any medication such as amoxicillin if one has had a reaction to penicillins or cephalosporins. If you keep getting rashes from these types of antibiotics, your doctor may recommend you to use an alternate drug other than amoxicillin. You can also use a topical corticosteroid ointment or cream to relieve the itchiness of the rash or take diphenhydramine (Benadryl) if the situation is appropriate. Cetirizine (Zyrtec) is another medication used to treat allergic rashes. If the rash is severe as described previously, urgent medical attention with a health professional and prompt treatment is advised as the side effects can be significant and life threatening.
Potential Treatment Options for Amoxicillin Rash in 2025
Treatment varies depending on the severity:
For Mild Rash (Non-Allergic):
- Antihistamines: Cetirizine (Zyrtec) or Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can reduce mild itching or discomfort.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Hydrocortisone cream may relieve mild skin irritation.
For Severe Rash (Suspected Allergic Reaction):
- Immediate Medical Attention: Hospital care, potentially epinephrine injections, steroids (e.g., prednisone), and IV antihistamines.
Always consult your healthcare provider before treating a rash, especially in children or individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is an amoxicillin rash able to spread to another person? No, amoxicillin rash is not communicable; it’s an immune or allergic reaction specific to the individual.
2. How long does an amoxicillin rash last? Typically, a mild rash resolves within 3-7 days after discontinuing the antibiotic. Severe reactions require prompt medical attention.
3. Should I stop amoxicillin if a rash appears? You should immediately contact your doctor. They will advise whether to continue or discontinue the medication based on the rash’s severity and your medical history.
4. Can I take cephalosporins if I had an amoxicillin rash? Cephalosporins might cause cross-reactivity. Always inform your healthcare provider of previous antibiotic reactions before starting a new medication.
Conclusion
In 2025, while amoxicillin remains widely prescribed and safe for most, it’s crucial to recognize and respond appropriately to potential skin reactions. Always monitor closely, seek medical guidance promptly when a rash appears, and disclose past reactions to antibiotics to your healthcare provider. Early intervention ensures safety and the best possible health outcomes.
More Umedoc Articles:
- 6 Powerful Facts About Amoxicillin Rash to Keep You Safe (2025)
- Sulfa Drug Rash (Bactrim Rash): Symptoms, Severity, and When to Worry (2025 Guide)
- Unpacking Weight Loss Medications: Beyond GLP-1s and Discount Cards
Resources:
NIH Stat Pearls https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459320/

This article reviewed by Dr. Jim Liu, MD and Ms. Deb Dooley, APRN.
There’s nothing more important than our good health – that’s our principal capital asset.
#medical #telehealth #amoxicillin #rash #umedoc